CSP Configuration
Configure Content Security Policy exceptions for your tools to access external resources while maintaining security.
Overview
Power Platform ToolBox implements per-tool Content Security Policy (CSP) configuration to allow tools to make external API calls and load external resources while maintaining security. This feature requires explicit user consent before granting any CSP exceptions.
What is CSP?
Content Security Policy (CSP) is a security standard that helps prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks and other code injection attacks by controlling which resources can be loaded by a web page.
By default, PPTB enforces a strict CSP for all tools:
- Scripts and styles can only be loaded from the tool itself
- Network requests can only be made to the tool itself
- Images can be loaded from the tool, data URIs, or HTTPS sources
- External fonts and other resources are restricted
Why Per-Tool CSP?
Some tools need to:
- Make API calls to other external services
- Load external libraries from CDNs (e.g., visualization libraries)
- Load external stylesheets or fonts
- Embed external content
Rather than weakening security for all tools, PPTB allows each tool to request only the specific CSP exceptions it needs, and users must explicitly grant these permissions.
How It Works
For Tool Users
- First Launch: When you launch a tool that requires CSP exceptions for the first time, you'll see a consent dialog
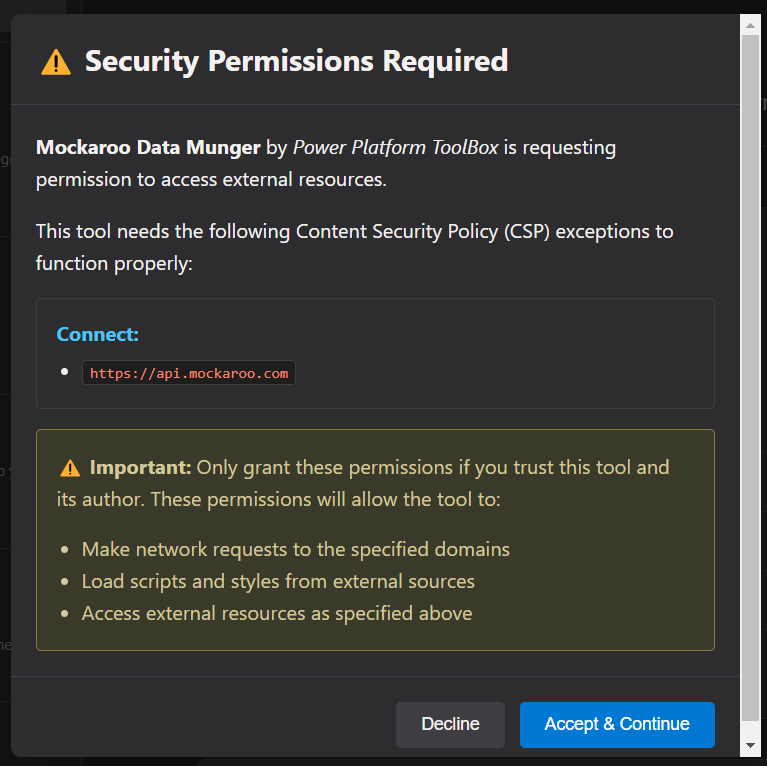
- Review Permissions: The dialog shows exactly what external resources the tool wants to access
- Grant or Decline: You can choose to accept or decline the permissions
- If you Accept: The tool will load with the requested CSP exceptions
- If you Decline: The tool will not load
- Stored Consent: If you accept, your consent is stored and you won't be asked again for that tool
- Security Enforcement: The system enforces that CSP exceptions are only applied if consent has been granted
- Revoke Consent: You can revoke consent at any time via the IPC API
For Tool Developers
Tools can specify CSP exceptions in their package.json manifest:
{
"name": "@power-maverick/dataverse-erd-generator",
"displayName": "Dataverse ERD Generator",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Generate Entity Relationship Diagrams from Dataverse",
"author": "Power Maverick",
"icon": "icons/test.svg",
"features": {
"minAPI": "1.2.0"
},
"cspExceptions": {
"connect-src": [
{
"domain": "https://*.dynamics.com",
"exceptionReason": "Required to **fetch** metadata and records from Dataverse."
},
{
"domain": "https://*.crm*.dynamics.com",
"exceptionReason": "Required to connect to region-specific Dataverse environments."
}
],
"script-src": [
{
"domain": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net",
"exceptionReason": "Loads the Mermaid diagram library used to render ERDs."
}
],
"style-src": [
{
"domain": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net",
"exceptionReason": "Loads Mermaid's bundled stylesheet.",
"optional": true
}
],
"img-src": [
{
"domain": "https://example.com/images",
"exceptionReason": "Displays entity icons in the diagram."
}
]
}
}
Security Considerations
Implementation Details
CSP Enforcement Flow:
- Tool's CSP exceptions are read from
package.jsonduring installation/loading - When a tool is launched, the system checks if it has CSP exceptions
- If exceptions exist, the system checks if user has granted consent
- If not granted, a consent dialog is shown to the user
- When the tool's HTML is served,
WebviewProtocolManagerchecks consent status - CSP exceptions are only applied if consent has been granted
- Without consent, the tool receives only the default restrictive CSP
This ensures that even if a tool declares CSP exceptions, they are not applied until the user explicitly grants permission.
For Users
- Only install tools from trusted sources
- Review CSP exceptions carefully before granting consent
- Watch for suspicious patterns like requests to unusual domains
- Revoke consent if you no longer use a tool
Developer Guidelines
- Never request
*or overly broad wildcards - Validate and sanitize all user input
- Use HTTPS for all external resources
- Keep dependencies up to date
- Follow the principle of least privilege
Supported CSP Directives
PPTB supports the following CSP directives for per-tool configuration. Each directive accepts an array of entries. An entry can be a plain string (just the domain) or an object with the following properties:
| Property | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
domain | string | Yes | The origin/domain to allow |
exceptionReason | string | No | Markdown description explaining why this CSP exception is needed. Supports markdown formatting and is displayed to users in the consent dialog. |
optional | boolean | No | When true, indicates that the core tool functions without this exception; granting it enables additional features. Defaults to false. |
- Name
connect-src- Type
- string | object[]
- Description
Controls which URLs can be loaded via XHR, fetch, WebSocket, etc.
[ { "domain": "https://*.dynamics.com", "exceptionReason": "Fetches metadata and records from Dataverse." } ]
- Name
script-src- Type
- string | object[]
- Description
Controls which sources can load JavaScript.
[ { "domain": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net", "exceptionReason": "Loads the Mermaid diagram library." } ]
- Name
style-src- Type
- string | object[]
- Description
Controls which sources can load CSS.
[ { "domain": "https://fonts.googleapis.com", "exceptionReason": "Provides the UI font family.", "optional": true } ]
- Name
img-src- Type
- string | object[]
- Description
Controls which sources can load images.
[ { "domain": "https://example.com/images", "exceptionReason": "Displays entity icons in the diagram." } ]
- Name
font-src- Type
- string | object[]
- Description
Controls which sources can load fonts.
[ { "domain": "https://fonts.gstatic.com", "exceptionReason": "Serves the UI font files.", "optional": true } ]
- Name
frame-src- Type
- string | object[]
- Description
Controls which sources can be embedded in frames.
[ { "domain": "https://trusted-domain.com", "exceptionReason": "Embeds the interactive report viewer." } ]
- Name
media-src- Type
- string | object[]
- Description
Controls which sources can load video/audio.
[ { "domain": "https://media-cdn.com", "exceptionReason": "Streams tutorial videos within the tool.", "optional": true } ]
Default CSP Policy
Tools start with this default CSP policy:
default-src 'self';
script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline';
style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline';
img-src 'self' data: https:;
font-src 'self' data:;
connect-src 'self';
Tool-specified exceptions are added to these defaults, not replaced.
Best Practices
1. Request Only What You Need
Only request CSP exceptions for resources your tool actually needs. Users are more likely to trust tools that request minimal permissions.
{
"cspExceptions": {
"connect-src": ["*"], // Too broad!
"script-src": ["*"] // Dangerous!
}
}
{
"cspExceptions": {
"connect-src": [
{
"domain": "https://api.powerbi.com",
"exceptionReason": "Embeds Power BI reports."
},
{
"domain": "https://*.dynamics.com",
"exceptionReason": "Fetches Dataverse metadata."
}
],
"script-src": [
{
"domain": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mermaid@9",
"exceptionReason": "Loads the Mermaid diagram library."
}
]
}
}
2. Use Specific Domains
Use the most specific domain patterns possible. Wildcards should be used sparingly.
- Prefer:
https://cdn.example.com - Over:
https://*.example.com - Avoid:
https:(allows any HTTPS site)
3. Document Your Requirements
Use the exceptionReason property on each entry to explain why your tool needs the exception. This description supports markdown and is shown to users in the consent dialog, helping them make an informed decision.
"cspExceptions": {
"connect-src": [
{
"domain": "https://*.dynamics.com",
"exceptionReason": "Required to **fetch metadata** from Dataverse"
}
],
"script-src": [
{
"domain": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net",
"exceptionReason": "Required to load the **Mermaid** diagram library"
}
]
}
Mark any exception as "optional": true when the core tool works without it and it only enables additional functionality:
"cspExceptions": {
"style-src": [
{
"domain": "https://fonts.googleapis.com",
"exceptionReason": "Loads the preferred UI font. The tool works with the system font if this is declined.",
"optional": true
}
]
}
4. Consider Alternatives
Before requesting CSP exceptions, consider if there are alternatives:
- Can you bundle the library instead of loading from CDN?
- Can you proxy API calls through a secure backend?
- Can you use PPTB's built-in Dataverse API instead of direct calls?
Revoking Consent
This is planned for future releases.
Users can revoke CSP consent for any tool:
- Go to Settings
- Navigate to Security / CSP Permissions (future feature)
- Find the tool and click "Revoke Consent"
- The next time the tool is launched, the consent dialog will appear again
Alternatively, consent is stored in the user settings file and can be manually edited.
Registry Configuration
When publishing a tool to the PPTB registry, include the cspExceptions in your registry entry:
{
"id": "dataverse-erd-generator",
"name": "Dataverse ERD Generator",
"version": "1.0.0",
"author": "Power Maverick",
"downloadUrl": "...",
"cspExceptions": {
"connect-src": [
{
"domain": "https://*.dynamics.com",
"exceptionReason": "Fetches metadata and records from Dataverse."
}
],
"script-src": [
{
"domain": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net",
"exceptionReason": "Loads the Mermaid diagram library."
}
]
}
}
Local tools can also specify CSP exceptions in their package.json. The same consent flow applies when loading local development tools.
Troubleshooting
Tool Shows CSP Violation Errors
Symptom: Browser console shows CSP violation errors
Solution:
- Check if you've granted CSP consent for the tool
- Verify the tool's CSP exceptions include the blocked resource
- Contact the tool developer if the exceptions are incorrect
CSP Dialog Doesn't Appear
Symptom: Tool doesn't load but no consent dialog is shown
Solution:
- Check browser console for JavaScript errors
- Clear the tool from the open tabs and try again
- Check if consent was already granted in settings
Can't Revoke Consent
Symptom: Want to revoke consent but can't find the option
Solution:
- Use the developer console:
window.toolboxAPI.revokeCspConsent('tool-id') - Manually edit the settings file located in the app's user data directory
- Full UI for consent management is planned for a future release
Complete Example
Here's a complete example for a tool that needs Dataverse access and external libraries:
{
"name": "@your-org/your-tool",
"displayName": "My Awesome Tool",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "A tool that does amazing things with Dataverse",
"author": "Your Name",
"main": "dist/index.html",
"icon": "icons/test.svg",
"features": {
"minAPI": "1.2.0"
},
"cspExceptions": {
"connect-src": [
{
"domain": "https://*.dynamics.com",
"exceptionReason": "Required to **fetch metadata and records** from Dataverse."
},
{
"domain": "https://*.crm*.dynamics.com",
"exceptionReason": "Required to connect to region-specific Dataverse environments."
}
],
"script-src": [
{
"domain": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mermaid@10",
"exceptionReason": "Loads the **Mermaid** library used to render entity relationship diagrams."
}
],
"style-src": [
{
"domain": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/mermaid@10",
"exceptionReason": "Loads Mermaid's bundled stylesheet for diagram rendering.",
"optional": true
}
]
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "https://github.com/your-org/your-tool"
},
"license": "MIT"
}
Future Enhancements
Planned improvements for CSP configuration:
- UI for Managing Consent - Settings page to view and revoke all CSP consents
- Temporary Consent - Option to grant one-time permission
- Detailed Audit Log - Track when tools use their CSP permissions
- CSP Templates - Pre-approved templates for common use cases (e.g., "Dataverse Access")
- Warning Levels - Different UI treatment for low-risk vs high-risk permissions