Tool Installation & Management
Power Platform ToolBox uses a marketplace-style registry system for discovering and installing tools. Learn how to find, install, update, and manage tools.
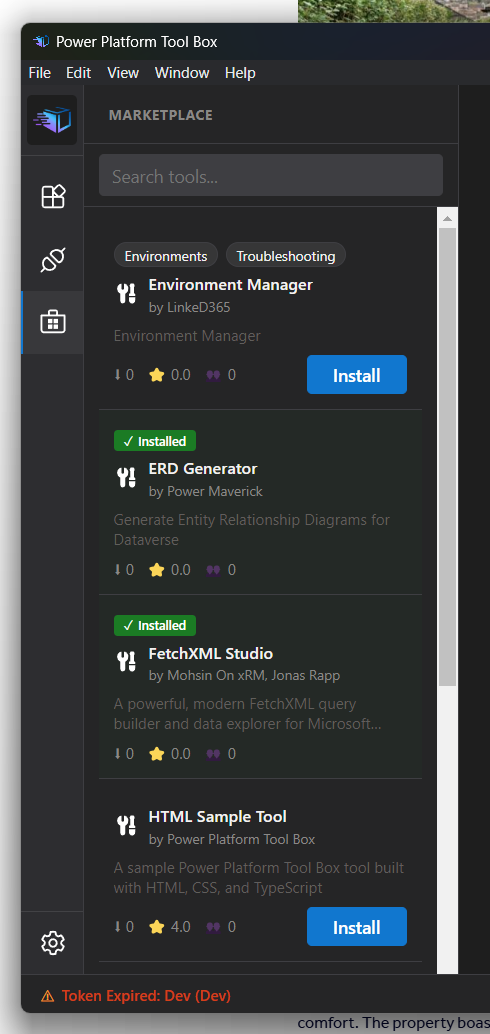
Tool Marketplace
Discovering Tools
The Tools Marketplace provides a centralized catalog of available tools:
- Click "Tools Marketplace" in the sidebar
- Browse featured tools or search by name, author, or category
- Select a tool to view details
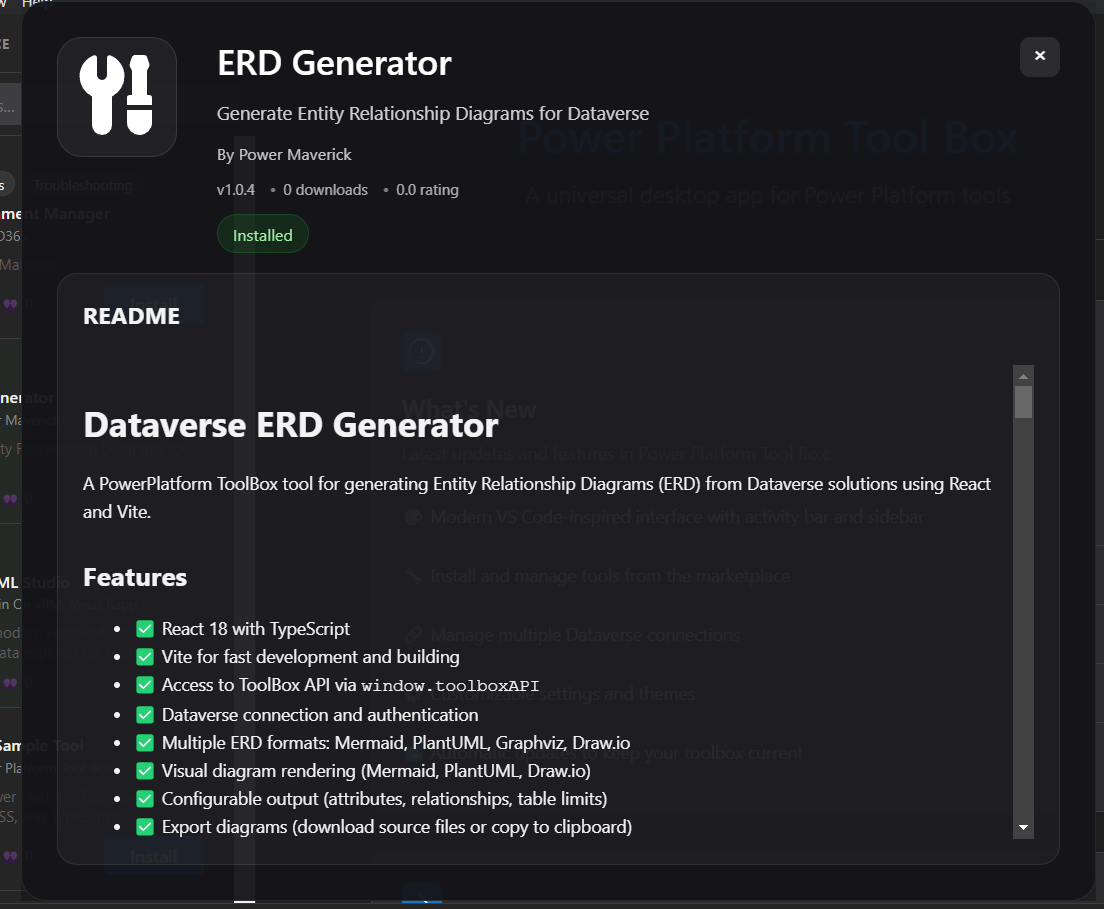
- Name and description
- Author and version
- Download count
- Required permissions (if any above Dataverse access)
- An author provided description of the tool
- Screenshots (if available)
- Click "Install" to add the tool to your PPTB installation
Tools are downloaded as pre-built packages from the PPTB registry. No npm or pnpm installation required on your machine.
Additional Installation Methods
For developers or private tools, PPTB supports installing directly from npm packages or your local filesystem.
Installing from npm or local files is intended for development and testing purposes only. Use the marketplace whenever possible.
Both these methods require the Show Debug Setting to be enabled in Settings menu.
From npm (For Development & Private Packages)
For debugging, development, or installing private npm packages:
- Ensure pnpm is installed on your system
- Open Debug / Install by Package in the sidebar
- Within the Install Tool by Package name, enter package name as shown on https://www.npmjs.com/
(e.g.,@your-org/your-tool) - Click "Install Package"
- PPTB installs via pnpm
- Tool loads after installation
From Local Files
For tool developers
- Ensure pnpm is installed on your system
- Open Debug / Install by Package in the sidebar
- Click browse and select the folder where your tool is, this is usually the root folder of your tool project
- Click "Load Tool"
- PPTB installs the local tool
- Tool loads after installation
Use this method for testing local tools during development or installing private npm packages not available in the marketplace.
Managing Installed Tools
View Installed Tools
The Installed Tools panel shows all installed tools:
- Tool name and icon
- Version number
- Status (loaded, error, updating)
- Quick launch button
Launch a Tool
- Click on a tool in the Installed Tools panel
- Tool loads in the main workspace, asking for a connection
- Tool UI appears in main workspace area
- Tool can now interact with active connection(s)
Update a Tool
- The Installed Tools panel will show an update badge for tools that have an update available
- Click "Update" next to the tool
- New version of the tool will be downloaded and update old version
- The new version of the tool will be available
Updates are atomic - if an update fails, the previous version remains installed.
Uninstall a Tool
-
In the Installed Tools panel, click the trash icon next to the tool
-
Confirm uninstallation.
-
Tool and any stored preferences are removed
Tool Registry System
Power Platform ToolBox uses a VS Code-style marketplace architecture:
How It Works
1. Developer publishes tool to npm
↓
2. Registered developers submit their tool to PPTB registry via https://www.powerplatformtoolbox.com/submit-tool
↓
3. Automated validation checks package and data about the tool
↓
4. A manual review by the Power Platform ToolBox team will be completed
↓
5. Tool is approved and added to registry.
↓
6. Tool is available in PPTB marketplace
↓
7. Installation downloads pre-built archive
↓
8. Tool extracted and cached locally
↓
9. Tool appears in Installed Tools panel
Registry Features
- Pre-built Archives: Tools distributed as ready-to-run packages
- Version Management: Track and install specific versions
- Update Checks: Automatic detection of new versions
- Metadata: Rich descriptions, icons, screenshots
- Categories: Organize tools by function
- Search: Find tools quickly by name or description
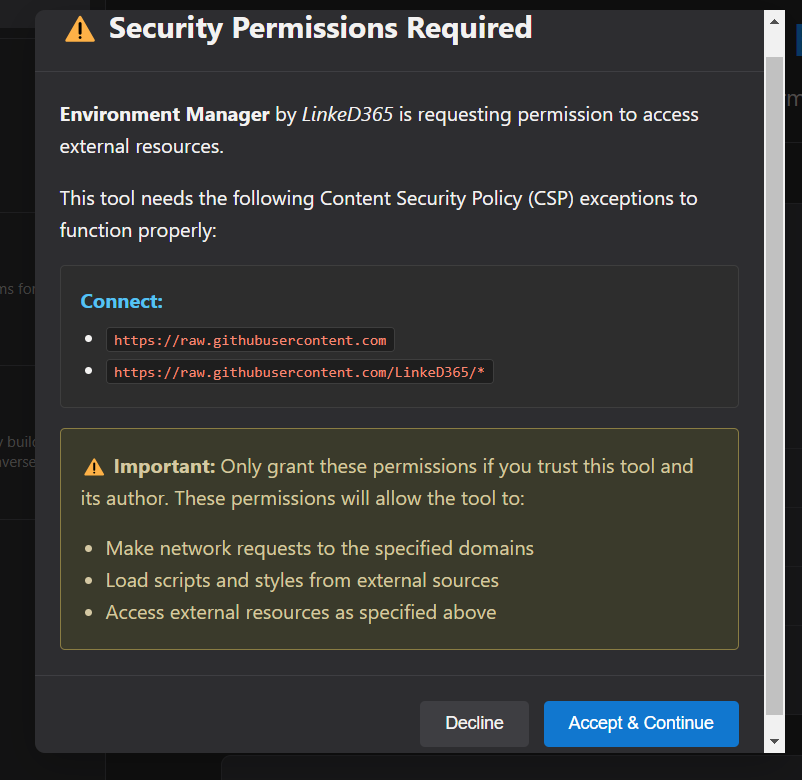
Tool Permissions
Tools may required additional permissions beyond standard Dataverse access.
The first time you launch the tool, or the required permissions change, you will see a permission consent dialog.
Review the requested permissions carefully before accepting.
Additional details on permissions, please see the Tool Developer documentation here.
If you decline, the tool won't load. If you accept, your choice is saved and you won't see the dialog again for that tool, unless the permissions requested change.
Staying Safe
Follow these best practices when reviewing CSP exceptions:
- Name
Review Carefully- Description
Read what the tool is requesting access to. Does it make sense for what the tool does?
- Name
Trust the Source- Description
Only grant exceptions to tools from developers you trust or tools with good reviews in the marketplace.
- Name
Watch for Red Flags- Description
Be suspicious if a simple tool requests access to many unrelated domains or services.
- Name
Revoke Anytime- Description
You can revoke CSP permissions at any time in the tool settings if you change your mind.
Example Scenarios
Here are common, legitimate reasons tools request CSP exceptions:
Scenario 1: Data Visualization Tool
Requests: script-src from https://cdn.jsdelivr.net
Reason: Loads a charting library to create graphs
Scenario 2: Custom Branding Tool
Requests: font-src from https://fonts.googleapis.com
style-src from https://fonts.googleapis.com
Reason: Uses custom web fonts for professional appearance
Permissions are tool-specific, not global. Granting access for one tool doesn't affect other tools' permissions.
Troubleshooting
Tool Won't Install
Symptom: Installation fails or hangs
Solutions:
- Check internet connectivity
- Verify registry server is accessible
- Check disk space is sufficient
- Try closing and reopening PPTB
- Check logs for specific errors
Tool Won't Load
Symptom: Tool installed but won't launch
Solutions:
- Ensure Node.js 18+ is installed
- Check tool compatibility with PPTB version
- Look for errors in developer console
- Try uninstalling and reinstalling
- Report issue to tool author
Tool Updates Fail
Symptom: Update downloads but doesn't apply
Solutions:
- Close the tool before updating
- Check write permissions in tool directory
- Verify sufficient disk space
- Manually uninstall and reinstall
Missing Dependencies
Symptom: Tool reports missing dependencies
Solutions:
- Registry packages should be self-contained
- Report issue to tool author
- Check tool's npm package configuration
- Try reinstalling from marketplace